| Bos taurus Gene: NOD1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InnateDB Gene | IDBG-633439.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last Modified | 2014-10-13 [Report errors or provide feedback] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Symbol | NOD1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Name | Uncharacterized protein | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Bos taurus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl Gene | ENSBTAG00000038235 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Encoded Proteins |
nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 1
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Protein Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Useful resources | Stemformatics EHFPI ImmGen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InnateDB Annotation from Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Summary |
[Homo sapiens] NOD1 and NOD2 represent central players in the control of the immune responses to bacterial infections and inflammation.
[Homo sapiens] NOD1 and NOD2 can induce CCL5 (RANTES) through NF-kappaB pathway, orchestrating the global Nod-dependent immune defence during bacterial infections.
[Homo sapiens] NOD1 and NOD2 direct autophagy by recruiting ATG16L1 to the plasma membrane at the site of bacterial entry.
[Homo sapiens] NOD1 plays an important role in host defence against bacterial infection by regulating direct killing of Helicobacter pylori bacteria by antimicrobial peptides.
[Homo sapiens] NOD1-dependent responses account for host resistance against T. cruzi infection by mechanisms independent of cytokine production.
[Homo sapiens] NOD1 plays a role in priming innate defences, facilitating a rapid response to infection by recognizing peptidoglycan from microbiota and enhancing killing of pathogens by bone marrow-derived neutrophils.
[Homo sapiens] NOD1 is a peripheral peptidoglycan intracellular sensor and is important for the progression and pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (animal model of multiple sclerosis).
[Homo sapiens] NOD1 detects heat-killed Legionella pneumophila and stimulates NFkB and IFN-beta promoter activity. NOD1 deficiency results in impaired bacterial clearance and increased proinflammatory cytokine at 24hrs post-infection. (Demonstrated in murine model)
[Homo sapiens] NOD1 is expressed by trophoblast cells across gestation and may have a role in mediating infection-associated inflammation and prematurity. Activation of NOD1 by bacterial peptidoglycan-derived peptide induces maternal-fetal inflammation and preterm labour.
[Homo sapiens] Nod1 KO mice were protected from high-fat diet induced inflammation, lipid accumulation, and peripheral insulin intolerance. Ex vivo, NOD1 activation by bacterial peptidoglycan mimetics induces proinflammatory cytokine secretion and impaired insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in adipocytes. Hence, NOD1 is a plausible, new link between innate immunity and metabolism. (Demonstrated in murine model)
[Homo sapiens] Helicobacter pylori infection of gastric epithelial cells activates NOD1 to enhance IFN-gamma signalling.
[Mus musculus] Nod1 and Nod2 activation results in substantial secretion of Ccl5 by murine macrophages and induces binding of NF-kappaB subunits to Ccl5 promoter.
[Mus musculus] Nod1 can activate the ISGF3 signaling pathway that is usually associated with protection against viral infection to provide mice with robust type I IFN-mediated protection from H. pylori and possibly other mucosal infections.
[Mus musculus] Nod1 and Nod2 account for neutrophil recruitment to the lungs of mice infected with Legionella pneumophila.
[Mus musculus] Nod1 and Nod2 can detect Legionella pneumophila and these receptors modulate the in vivo pulmonary immune response differently.
[Mus musculus] Nod1 is a peripheral peptidoglycan intracellular sensor and is important for the progression and pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (animal model of multiple sclerosis).
[Mus musculus] Nod1 detects heat-killed Legionella pneumophila and stimulates NFkB and IFN-beta promoter activity. Nod1 deficiency results in impaired bacterial clearance and increased proinflammatory cytokine at 24hrs post-infection.
[Mus musculus] Nod1 is expressed by trophoblast cells across gestation and may have a role in mediating infection-associated inflammation and prematurity. Activation of Nod1 by bacterial peptidoglycan-derived peptide induces maternal-fetal inflammation and preterm labour.
[Mus musculus] Nod1 KO mice were protected from high-fat diet induced inflammation, lipid accumulation, and peripheral insulin intolerance. Ex vivo, Nod1 activation by bacterial peptidoglycan mimetics induces proinflammatory cytokine secretion and impaired insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in adipocytes. Hence, Nod1 is a plausible, new link between innate immunity and metabolism.
[Mus musculus] Nod1 and Nod2 synergize with Tlr4 in dendritic cells to increase IL12 production and enhance invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cell activation, and are important regulators of the IFN gamma response by iNKT cells during S. typhimurium and L. monocytogenes infections.
[Mus musculus] Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium Î?msbB that possesses a modified lipid A triggers exacerbated colitis in the absence of Nod1 and/or Nod2, which is likely due to increased Tlr2 stimulation.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entrez Gene | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Summary |
This gene does not have any Entrez summary - the following is the summary from its human ortholog ENSG00000106100:
This gene encodes a member of the NOD (nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain) family. This member is a cytosolic protein. It contains an N-terminal caspase recruitment domain (CARD), a centrally located nucleotide-binding domain (NBD), and 10 tandem leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) in its C terminus. The CARD is involved in apoptotic signaling, LRRs participate in protein-protein interactions, and mutations in the NBD may affect the process of oligomerization and subsequent function of the LRR domain. This protein is an intracellular pattern-recognition receptor (PRR) that initiates inflammation in response to a subset of bacteria through the detection of bacterial diaminopimelic acid. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants differring in the 5' UTR have been described, but the full-length nature of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009] This gene encodes a member of the NOD (nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain) family. This member is a cytosolic protein. It contains an N-terminal caspase recruitment domain (CARD), a centrally located nucleotide-binding domain (NBD), and 10 tandem leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) in its C terminus. The CARD is involved in apoptotic signaling, LRRs participate in protein-protein interactions, and mutations in the NBD may affect the process of oligomerization and subsequent function of the LRR domain. This protein is an intracellular pattern-recognition receptor (PRR) that initiates inflammation in response to a subset of bacteria through the detection of bacterial diaminopimelic acid. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants differring in the 5\' UTR have been described, but the full-length nature of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | Protein coding | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Genomic Location | Chromosome 4:66275926-66311831 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Strand | Forward strand | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Band | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transcripts |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interactions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of Interactions |
This gene and/or its encoded proteins are associated with 0 experimentally validated interaction(s) in this database.
They are also associated with 27 interaction(s) predicted by orthology.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Ontology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Function |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Process |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Component |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Species
Homo sapiens
Mus musculus
|
Gene ID
Gene Order
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathway Predictions based on Human Orthology Data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NETPATH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| REACTOME |
JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 pathway
activated TAK1 mediates p38 MAPK activation pathway
TAK1 activates NFkB by phosphorylation and activation of IKKs complex pathway
MyD88-independent cascade pathway
Toll Like Receptor 3 (TLR3) Cascade pathway
MyD88:Mal cascade initiated on plasma membrane pathway
Toll Like Receptor TLR1:TLR2 Cascade pathway
Toll Like Receptor TLR6:TLR2 Cascade pathway
TRAF6 mediated induction of NFkB and MAP kinases upon TLR7/8 or 9 activation pathway
MyD88 dependent cascade initiated on endosome pathway
Toll Like Receptor 9 (TLR9) Cascade pathway
MyD88 cascade initiated on plasma membrane pathway
Toll Like Receptor 10 (TLR10) Cascade pathway
Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Cascade pathway
Toll Like Receptor 5 (TLR5) Cascade pathway
NOD1/2 Signaling Pathway pathway
Interleukin-1 signaling pathway
Toll Like Receptor 7/8 (TLR7/8) Cascade pathway
Cytokine Signaling in Immune system pathway
Innate Immune System pathway
Toll Like Receptor 2 (TLR2) Cascade pathway
Toll-Like Receptors Cascades pathway
MAP kinase activation in TLR cascade pathway
Nucleotide-binding domain, leucine rich repeat containing receptor (NLR) signaling pathways pathway
Immune System pathway
Signaling by Interleukins pathway
Activated TLR4 signalling pathway
TRIF-mediated TLR3/TLR4 signaling pathway
Toll Like Receptor 3 (TLR3) Cascade pathway
TRAF6 mediated induction of NFkB and MAP kinases upon TLR7/8 or 9 activation pathway
Toll Like Receptor 2 (TLR2) Cascade pathway
Innate Immune System pathway
JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 pathway
MyD88 cascade initiated on plasma membrane pathway
Cytokine Signaling in Immune system pathway
Toll Like Receptor TLR1:TLR2 Cascade pathway
MAP kinase activation in TLR cascade pathway
Immune System pathway
Toll Like Receptor 5 (TLR5) Cascade pathway
Toll Like Receptor TLR6:TLR2 Cascade pathway
activated TAK1 mediates p38 MAPK activation pathway
Toll Like Receptor 9 (TLR9) Cascade pathway
Toll-Like Receptors Cascades pathway
Signaling by Interleukins pathway
NOD1/2 Signaling Pathway pathway
MyD88 dependent cascade initiated on endosome pathway
Nucleotide-binding domain, leucine rich repeat containing receptor (NLR) signaling pathways pathway
Activated TLR4 signalling pathway
Interleukin-1 signaling pathway
MyD88-independent cascade pathway
Toll Like Receptor 7/8 (TLR7/8) Cascade pathway
MyD88:Mal cascade initiated on plasma membrane pathway
TRIF-mediated TLR3/TLR4 signaling pathway
TAK1 activates NFkB by phosphorylation and activation of IKKs complex pathway
Toll Like Receptor 10 (TLR10) Cascade pathway
Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Cascade pathway
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG |
Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection pathway
NOD-like receptor signaling pathway pathway
Shigellosis pathway
NOD-like receptor signaling pathway pathway
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INOH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PID NCI | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SwissProt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TrEMBL | E1B7V7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt Splice Variant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entrez Gene | 781426 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniGene | Bt.42716 Bt.89027 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq | NM_001256563 XM_005205508 XM_005205509 XM_598513 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HUGO | HGNC:16390 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CCDS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HPRD | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IMGT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EMBL | DAAA02010901 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GenPept | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
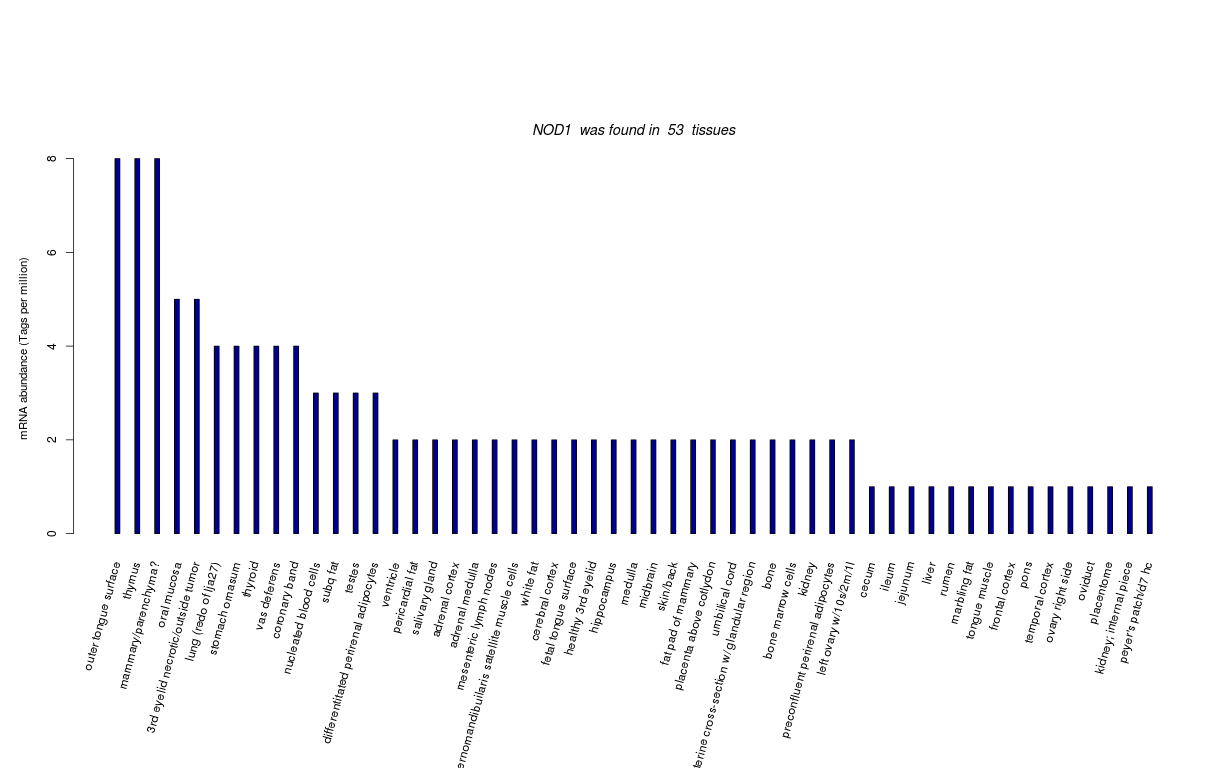
| RNA Seq Atlas | 520275 781426 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transcript Frequencies | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tag Count based mRNA-Abundances across 87 different Tissues (TPM).
Based on Data from Bovine Gene Atlas |
(Move your mouse over the image to view a more detailed version) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||